Bridging Gaps in Medical Access Through Telehealth

In recent years, telehealth has emerged as a groundbreaking solution to bridge the gaps in medical access. This innovative approach leverages technology to provide healthcare services remotely, offering significant benefits to patients and healthcare providers alike. Let’s explore how telehealth is transforming the healthcare landscape, making medical access more efficient and effective.
The Evolution of Telehealth
From Concept to Reality
Telehealth, once a futuristic concept, has now become a mainstream mode of delivering healthcare. The term encompasses a wide range of services, including virtual consultations, remote patient monitoring, and mobile health applications. This evolution has been driven by advances in technology, changes in healthcare policies, and a growing recognition of the need for more flexible healthcare delivery models.
Key Drivers of Telehealth Adoption
Several factors have contributed to the rapid adoption of telehealth:
- Technological Advancements: High-speed internet, smartphones, and video conferencing technologies have made telehealth feasible and reliable.
- Policy Changes: Regulatory changes and reimbursement policies have facilitated the integration of telehealth into the healthcare system.
- Pandemic Impact: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telehealth as social distancing measures necessitated remote healthcare solutions.
Benefits of Telehealth
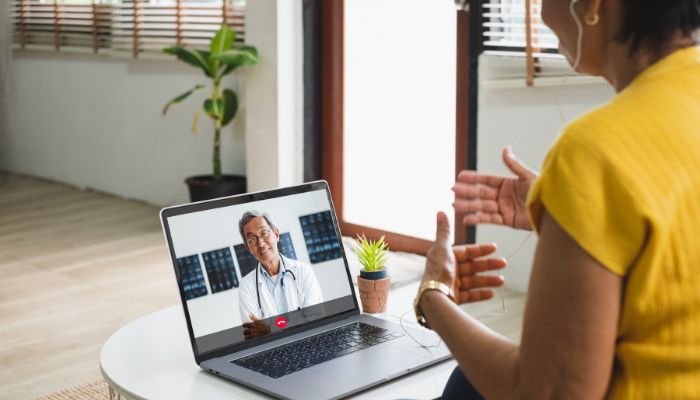

Increased Access to Care
Telehealth breaks down geographical barriers, allowing patients in remote or underserved areas to access medical care. This is particularly beneficial for individuals living in rural areas who might otherwise have to travel long distances to see a healthcare provider.
Convenience and Flexibility
Patients can schedule appointments at their convenience, reducing the need for time off work or long waits in a doctor’s office. This flexibility is especially valuable for those with busy schedules or mobility issues.
Continuity of Care
Telehealth enables continuous monitoring and follow-up care, which is crucial for managing chronic conditions. Patients can easily connect with their healthcare providers for regular check-ins, medication adjustments, and advice, ensuring better health outcomes.
Cost Savings
Telehealth can reduce healthcare costs by minimizing the need for in-person visits, hospital admissions, and emergency room visits. Patients save on travel expenses and time, while healthcare systems can optimize resource utilization.
Telehealth Applications
Virtual Consultations
One of the most common applications of telehealth is virtual consultations. Patients can connect with healthcare providers via video calls for routine check-ups, consultations, and follow-ups. This is particularly useful for non-emergency situations, mental health consultations, and managing chronic conditions.
Remote Patient Monitoring
Telehealth technologies enable remote monitoring of patients’ vital signs, such as blood pressure, glucose levels, and heart rate. Devices like wearable sensors and mobile apps collect and transmit data to healthcare providers, allowing for timely interventions and personalized care plans.
Mobile Health Applications
Mobile health apps provide patients with tools to manage their health, such as medication reminders, fitness tracking, and access to medical information. These apps empower patients to take an active role in their health management.
Telehealth for Specialized Care
Telehealth also facilitates access to specialized care, such as telepsychiatry, teledermatology, and telecardiology. Patients can receive expert consultations without the need to travel to specialized centers, ensuring timely and effective treatment.
Challenges and Solutions
Technological Barriers
While telehealth offers numerous benefits, it also presents challenges, particularly in terms of technology. Not all patients have access to high-speed internet or the necessary devices. Addressing this digital divide requires investment in infrastructure and initiatives to provide affordable technology solutions.
Regulatory and Reimbursement Issues
The regulatory landscape for telehealth is complex and varies by region. Ensuring consistent and favorable reimbursement policies is crucial for the sustainability of telehealth services. Advocacy and collaboration among stakeholders can help streamline regulations and ensure fair compensation for telehealth providers.
Patient and Provider Acceptance
Both patients and healthcare providers need to be comfortable with telehealth technologies. Education and training programs can help increase acceptance and proficiency in using telehealth platforms. Building trust through secure and user-friendly interfaces is also essential.
Future of Telehealth

Integration with Traditional Healthcare
The future of telehealth lies in its integration with traditional healthcare. Hybrid models that combine in-person and virtual care can offer the best of both worlds, ensuring comprehensive and patient-centered care. Healthcare systems must adapt to these hybrid models to maximize the benefits of telehealth.
Advancements in Telehealth Technologies
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are poised to revolutionize telehealth. These technologies can enhance diagnostic accuracy, personalize treatment plans, and enable proactive health management.
Expanding Telehealth Services
As telehealth continues to evolve, we can expect an expansion in the types of services offered. From telepharmacy to tele-rehabilitation, the possibilities are vast. This expansion will further enhance the accessibility and quality of healthcare.
Conclusion
Telehealth is a powerful tool that is reshaping the healthcare landscape. By bridging gaps in medical access, it offers numerous benefits, including increased convenience, cost savings, and improved health outcomes. While challenges remain, ongoing advancements in technology and supportive policies will continue to drive the growth and integration of telehealth. As we move forward, telehealth will play an increasingly vital role in delivering accessible, efficient, and effective healthcare for all.
Also Read;



Leave feedback about this